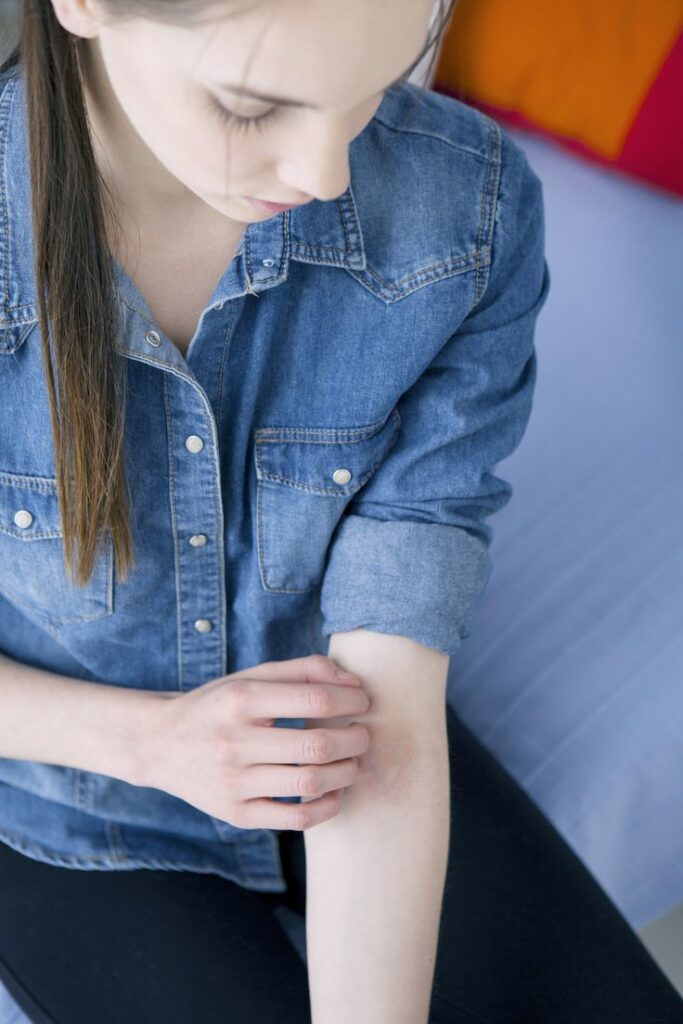
Eczema is an increasingly prevalent skin condition affecting millions of individuals worldwide, often genetics-, environment- and immune-driven conditions that play a part in flare ups; yet many underestimate how diet – specifically histamine rich foods- can influence allergic eczema outbreaks and which ones need to be avoided for good skin health. This article looks into these topics further and suggests foods you might want to try avoiding as a solution for managing their symptoms of allergic eczema.
What Is Histamine?
Histamine is a natural chemical produced in your body when experiencing an allergic response. This substance works to defend against allergens by expanding blood vessels and making them more permeable, leading to classic allergy symptoms like itching, redness and swelling.
Histamine can be found in many everyday foods and some people may have difficulty breaking it down in the gut, leading to intolerance of this compound. Consuming high-histamine foods might further aggravate symptoms for those suffering with eczema and lead to more frequent or severe flare-ups of skin inflammation.
Understanding Histamine Intolerance and Eczema
Histamine intolerance occurs when either too much histamine is produced in the body or its breakdown cannot take place efficiently enough, due to reduced diamine oxidase (DAO) enzyme levels in your system reducing output of histamine intolerance; when this happens, histamine builds up within your cells leading to symptoms including:
Skin rashes or hives, itching, digestive issues, headaches and flushed skin are some of the symptoms associated with Eczema; any additional histamine in our system could aggravate symptoms further and delay healing times.
Histamine-Rich Foods to Watch Out For
Many seemingly healthy and nutritional foods contain surprising high concentrations of histamine; if your allergic eczema appears related to diet, consider restricting or eliminating these histamine-rich items:
Aged and fermented foods contain higher histamine concentrations due to fermentation processes: these items tend to rank highly on histamine lists.
Aged cheeses (parmesan, gouda and cheddar) provide excellent tasting varieties.
Yogurt, Kefir and Sauerkraut. Soy Sauce and Miso
1.Cured and Processed Meats
Salami, Ham, Bacon and Smoked or canned fish may all contain ingredients that significantly raise histamine levels when consumed as part of their usual preparation processes.
2.Certain Vegetables and Fruits
Although fruits and vegetables in general tend to be beneficial, certain ones may trigger histamine-related symptoms in individuals sensitive to histamine. These foods include asparagus and green bell pepper.
3.Avocados, spinach, tomatoes, eggplant and strawberries contain histamine-containing foods which also encourage your body to produce even more histamine – creating an exponential impactful response in your system.
4.Leftovers
Histamine levels increase with any food stored for long, even in the fridge – this is particularly evident for meats and seafood products.
Tips to Help Manage Histamine in Your Diet
1.Making diet changes may feel intimidating, but small steps can have an enormous impact. Here are a few suggestions to guide your process of change:
2.Prep meals from scratch to avoid unwanted leftovers and save yourself some extra effort in the kitchen.
3.Freeze extra portions immediately in order to prevent histamine formation and keep them away from becoming histamine-causing allergens.
4.Choose fresh meats and veggies over processed or aged alternatives.
5.Consider keeping a food diary to monitor reactions.
Before beginning any diet designed to lower histamine, consult with a healthcare provider or dietician first.
Supplements Can Provide Relief
Some individuals benefit from taking DAO enzyme supplements before meals to break down histamine in their digestive tract and reduce symptoms. Furthermore, vitamin C and quercetin are natural antihistamines known to bolster immunity and support its functions.
Final Thoughts
While histamine-rich foods don’t cause allergic eczema directly, they can serve as triggers that exacerbate symptoms for many sufferers. Knowing which to avoid and managing diet effectively may lead to improved skin health and reduced flare ups – with patience, planning, and awareness, living more comfortably–even with eczema!
SEE MORE:https://nutritionnest.site/wp-admin/post.php?post=599&action=edit
 healthybodyboost.net Healthy Body Boost
healthybodyboost.net Healthy Body Boost